What Is Application Level Gateway – The Utmost Guide on Application Gateways
What Is Application Layer Gateway?
Application Level Gateway (ALG) is nothing but security hardware also known as an application proxy gateway by filtering incoming node traffic. It is a part of a NAT router and acts on behalf of an app or network protecting them from malicious traffic to certain specifications. These specifications define that only transmitted information from the network app is filtered. Among such apps are FTP (File Transfer Protocol), Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP), Telnet, and BitTorrent.
ALG can perform a variety of functions at the app layer which is commonly known as layer 7 in the OSI model.
ALG can perform a variety of functions at the app layer which is commonly known as layer 7 in the OSI model.
These functions may include the process of data synchronization, traffic control, resource allocation, as well as address and port translation. Application security gateway acts like a proxy server and delivers app layer security by preventing or terminating connections when needed. Hence, the connection is secure because the user first connects with the proxy.
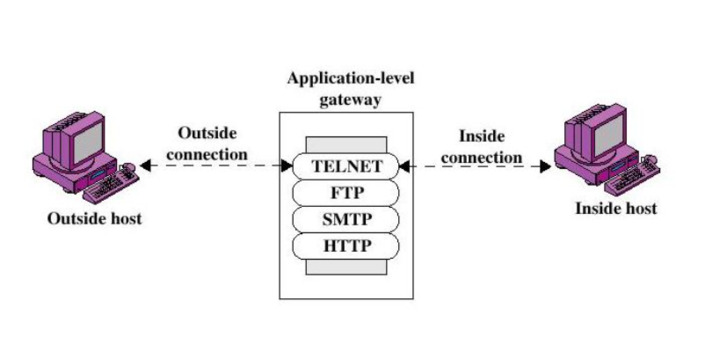
How Does Application Layer Gateway Work?
Being a component of a NAT router, Application Layer Gateway understands an app protocol. When packets of this protocol pass through it, it modifies them in such a way that users behind the NAT can use the protocol.
The NAT router relays packets coming from an external IP address inside the network. After passing the NAT, some parameters like port and address become incorrect. Consequently, the remote side cannot establish a connection.
Having identified the packet as belonging to this protocol, ALG substitutes its address and port instead of yours. If a remote computer establishes a connection on this port according to the protocol, retransmission is automatically enabled.
ALG is similar to a proxy server. It manages such protocols as SIP and FTP using deep inspection packets to detect and block attacks before the traffic passes to the app. Generally, the capacities of Application Gateways exceed those provided by firewalls.
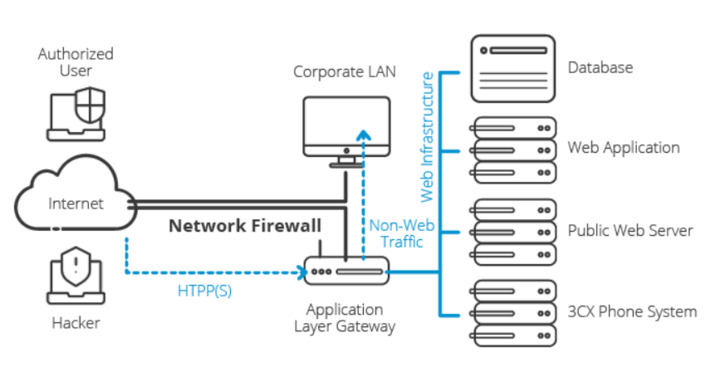
What Are the Key Functions of Application Layer Gateway?
- Usage of TCP/UDP port: Application Layer Gateway allows client apps to use dynamic ports to communicate with ports used by server apps. Unlike ALG, firewall configuration supports only a limited number of known ports. When there is no ALG used, the ports can become blocked. In this case, the network administrator will need to open a large number of ports in the firewall, which will make the network vulnerable to attacks.
- Conversion: ALG converts the network address information that is located between addresses acceptable on both sides of the NAT or firewall. This aspect introduces the term “gateway” for ALG.
- Full control over commands: The hardware recognizes the specific commands and requests and provides full control over them.
- Data synchronization: ALG synchronizes session data provided by two hosts exchanging data. For example, FTP apps can use separate connections to transmit and exchange data. During the transfer of large files, the control connection may remain free. ALG can prevent network devices from waiting for a control connection to expire before a long file transfer is completed.
Why Are Application Gateways Important?
ALG ensures connection security and provides additional protection from malicious traffic. Using this kind of hardware, you can preserve your business from attacks and keep your personally identifiable information (PII) safe from leakage. It is an option for defending apps and keeping crucial data secret.
Pros and Cons of Using Application Gateways
Pros
- The gateway expands the network by connecting different systems.
- It prevents data leakage and protects from malicious attacks by acting like an intermediary.
- These “protocole converters” change the data format to the required architecture.
- ALG controls the domain in terms of collision and broadcasting.
Cons
- Gateways are expensive and difficult to install and configure.
- It takes some time to get data translated and converted. Besides, gateways return all the cache information that was not used during the work which also takes some time.
- Computers dealing with different protocols must be fixed individually.
What Is Firewall?
A Firewall is hardware or software that decides whether to skip or block a passing data packet. Its main function is to block malicious activity and prevent unauthorized user actions both on the private network and outside it.
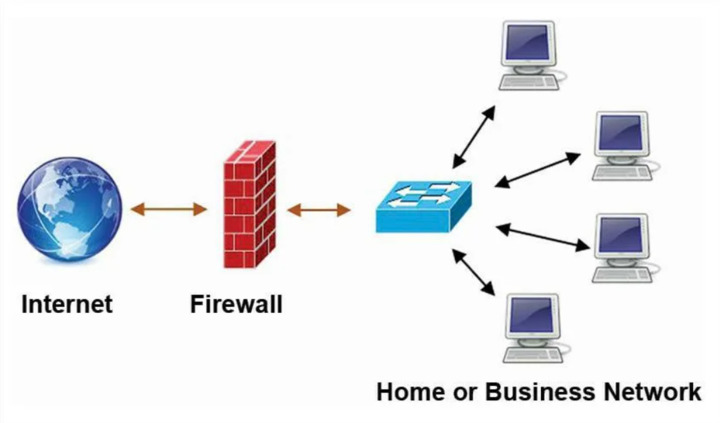
How Does Firewall Work?
The firewall works as a filter: it allows only filtered traffic out of the entire traffic flow. This is the first line of defensive fortifications between internal networks and external ones, such as the Internet. The need for firewalls arose when it became clear that the principle of complete connectivity of networks no longer works.
The firewall is designed to protect the internal information environment or its individual parts from some external flows, and vice versa protects against the passage of individual packets outside. Firewalls allow you to filter out suspicious and malicious traffic, including preventing attempts to hack and compromise data.
With proper configuration, the network shield allows network users to access the necessary resources. Also, it rejects unwanted connections from hackers, viruses, and other malware that are trying to break into a protected environment.
What Are the Firewall Functions?
- Filtering data: The Firewall distributes data packets by headers. The weakness of this approach is that if the packets are fragmented or there is an IP substitution. Hence, there is an opportunity to break through the protection.
- Gateway establishment: A Firewall establishes a gateway within the session between the recipient and the sender of the packet, but the contents of the packets are not controlled. Vulnerabilities are the same as the first type.
- Intermediary in the connection: the software monitors the contents of packets for transmitted commands and potentially unsafe instructions. The minus of this option is that they work relatively slowly and require a lot of computing power.
- Status inspection: it harmoniously analyzes data, taking advantage of all three of the above options.
Application Gateways vs Firewall
| Firewall | ALG |
| Can be either hardware or software | Only hardware |
| Secures a network | Protects the network and links separate networks together |
| Additional charges for extra nodes and server updates are required during installation. | Expensive but has a one-time cost |
| Do not convert data | Convert data |
| Guarantees privacy | Privacy depends on the password protection |
